Threat-Hunting in the Cloud: 10 Ways to Identify and Stop Threats in Your Cloud Environment
Cloud computing has digitally transformed the way businesses and organizations store, manage and process data. This has enabled greater agility, scalability and cost-effectiveness of the cloud as a business transformation solution.
However, with the increasing reliance on cloud services, organizations and businesses are also exposed to a broad range of cyber threats and security breaches that come in many different forms and can happen from a variety of sources. Threat hunting in the cloud is a good way to catch these potential threat scenarios.
In this blog, we will discuss - What Threat-Hunting in the Cloud is; How it Works and Why Use Cloud-based Threat-Hunting platforms to identify and prevent breaches across the enterprise.
What Threat-Hunting In the Cloud Is
Threat-hunting in the cloud refers to the proactive and systematic search for signs of an ongoing cyber attack or compromise within an organization's cloud infrastructure. It involves using a combination of security tools, techniques, and data analytics to identify and isolate potential security threats that may have evaded traditional security controls such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems. The goal of threat-hunting in the cloud is to detect and mitigate potential security incidents as early as possible, reducing the risk of data loss, business interruption, and damage to reputation.
Threat-hunting in the cloud requires an understanding of cloud architecture, a combination of technical skills, and the ability to identify and respond to anomalous threat behaviour.
How Threat-Hunting In the Cloud Works
It involves the following steps:
· Data Collection:
This is the first step in threat-hunting in the cloud. Data is collected from various sources, e.g. cloud activity logs, network traffic, and system logs. The data provides a comprehensive view of cloud activity and assists security teams identify patterns and anomalies.
· Data Analysis:
The second step is to analyze the collected data using AI (artificial intelligence) and ML (machine learning) algorithms. This automates the detection of anomalies and network traffic to identify suspicious activity and potential security threats.
· Threat Validation:
Security teams validate potential threats that have been identified to determine if the threat is real or a false positive. This will involve conducting further investigation using additional tools such as network intrusion detection systems to verify the findings.
· Response:
Security teams must respond quickly to identified and confirmed threats to contain the incident and prevent further damage. This may involve isolating the affected systems, restoring from backups, and implementing security updates and patches.
· Post-Incident Review:
At this stage, it is important to review incidents in other to discuss details of what went wrong, the impact, actions taken to resolve it and what could be improved to prevent similar incidents in the future. This may involve updating security policies and procedures, modifying security controls, and improving employee training.
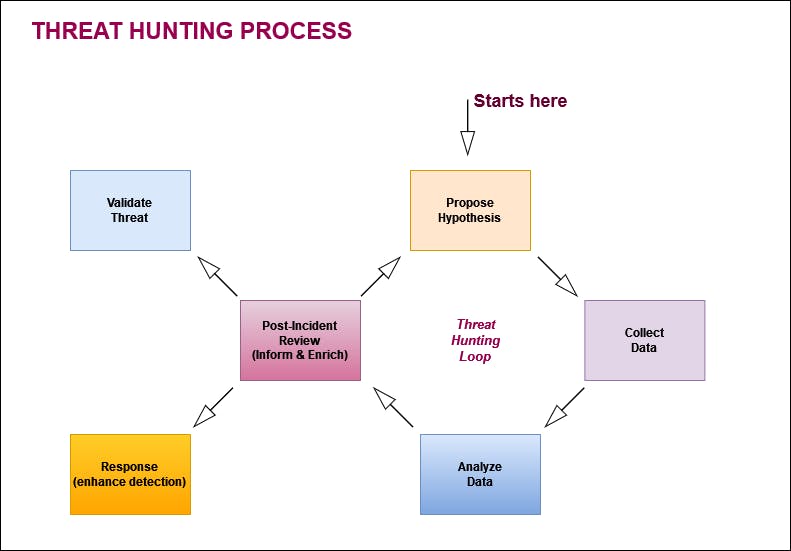
Fig 1: Overview of the Threat-Hunting Process
How to Setup a Threat-Hunting Program in the Cloud
1. Define the scope: Identify the cloud services, data, and systems that you want to monitor and protect.
2. Organize a team: Select a team of security subject matter experts with a mix of technical and analytical skills.
3. Establish visibility: Implement cloud security tools to provide real-time visibility into cloud activity e.g. cloud access security brokers (CASBs) and cloud security posture management (CSPM) solutions.
4. Implement a security architecture: Robust implementation of cloud security architecture that includes identity and access management (IAM), encryption, and data privacy.
5. Create a plan: Develop guidelines for conducting threat hunting in the cloud, including how you will collect and analyze data, validate threats, respond to incidents, and review incidents after they occur.
6. Monitor and review continuously: Your cloud environment should be monitored and reviewed continuously for signs of security incidents and update your threat-hunting process as required.
Threat hunting in the cloud is a continuous process that requires an understanding of cloud architecture, a combination of technical skills, and a proactive approach to identifying and mitigating cyber threats.
Why Use Cloud-based Threat Hunting platforms
Cloud-based threat-hunting platforms offer several benefits and advantages for identifying and preventing breaches across the enterprise:
a) Scalability: Cloud-based platforms can handle large amounts of data and provide the necessary resources to keep up with the growing needs of the organization.
b) Integration: They can easily integrate with existing security tools and infrastructure, providing a comprehensive security solution.
c) Real-time threat detection: Cloud-based threat-hunting platforms provide real-time monitoring and analysis of large data sets, allowing for quick identification of threats.
d) Automation: They can automate repetitive and manual tasks, freeing up security teams to focus on more strategic work.
e) Cost-effective: Cloud-based solutions are often more cost-effective compared to traditional on-premise solutions, as they don't require expensive hardware or maintenance costs.
f) Access to expertise: Cloud-based platforms often have teams of security experts who constantly monitor and update the platform to provide the latest threat intelligence and protection.
In retrospect, Cloud-based threat hunting platforms provide organizations with a comprehensive and cost-effective solution to identify and prevent security breaches.
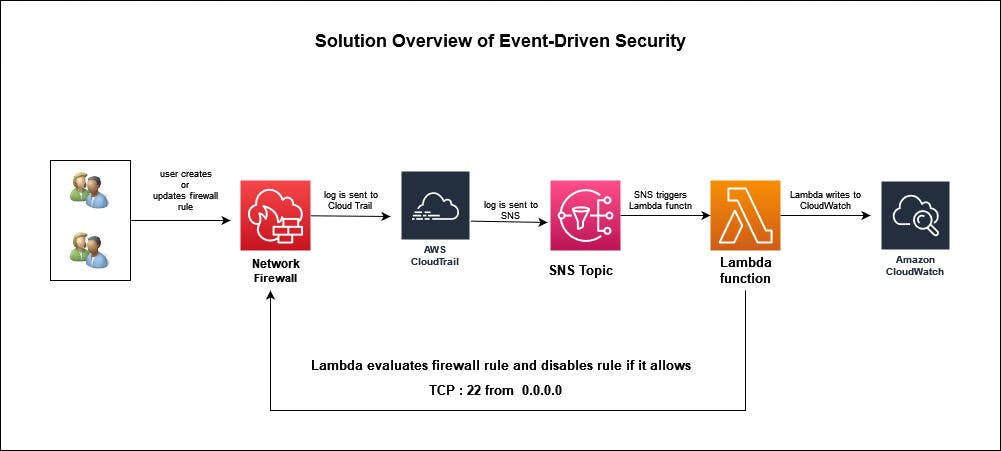
Fig 2: Use case of Automated/Event-Driven Security Solution (AWS Cloud)
Recommendations
Here are 10 best practices to identify and stop threats in a hybrid/multi-cloud environment:
1. Monitor logs and alerts continuously to identify any suspicious activity.
2. Use multi-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data.
3. Segment networks to reduce the attack surface and prevent the spread of threats.
4. Conduct regular security assessments to assess the security posture of cloud resources to identify vulnerabilities and potential threats.
5. Encrypt sensitive data to protect it from unauthorized access and to ensure data privacy.
6. Implement intrusion detection and prevention systems to detect and prevent network attacks.
7. Update software and infrastructure regularly to address known security vulnerabilities.
8. Regularly back up critical data to minimize the impact of a data loss event.
9. Implement strict and robust access controls to limit and monitor access to sensitive data based on the principle of least privilege for job roles/responsibilities.
10. Conduct regular security awareness training to educate and equip employees to identify and report potential threats.
Conclusion
Threat hunting in the cloud is a critical component of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. It helps organizations proactively detect and mitigate cyber threats within hybrid/multi-cloud environments before they cause significant damage. By implementing a secure cloud security architecture, investing in cloud security tools, and regularly reviewing cloud activity logs, organizations can enhance their threat-hunting capabilities and improve their overall security posture.