High Performance Network Computing: 5 Reasons Why BGP is the Perfect Technology Protocol for Businesses
Introduction
The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is a standardized exterior gateway protocol used for expressing the best path to reach any network from any other networks whether in a business or organization's own local area network environment or over the internet. It is an efficiently distributed routing system because of its lightweight, security and reliability.
It is also the primary routing protocol used in the Internet to exchange routes, reachability information, and to establish paths.
What is BGP?
The Border Gateway Protocol is often described as the “Internet’s phone book” as defined in the reference for comments (RFC 4271) which is currently used by the Internet community. It is also known as a messaging protocol that specifies message types and codes, message formats, message contents, and more. The protocol was designed to control the flow of traffic and to provide information about the networks between two autonomous entities, businesses or organizations.
Simply put, the border gateway is a router that is located at the edge of an autonomous system or local area network that allows devices in private networks belonging to users, businesses and organizations to connect to each other over the internet efficiently.
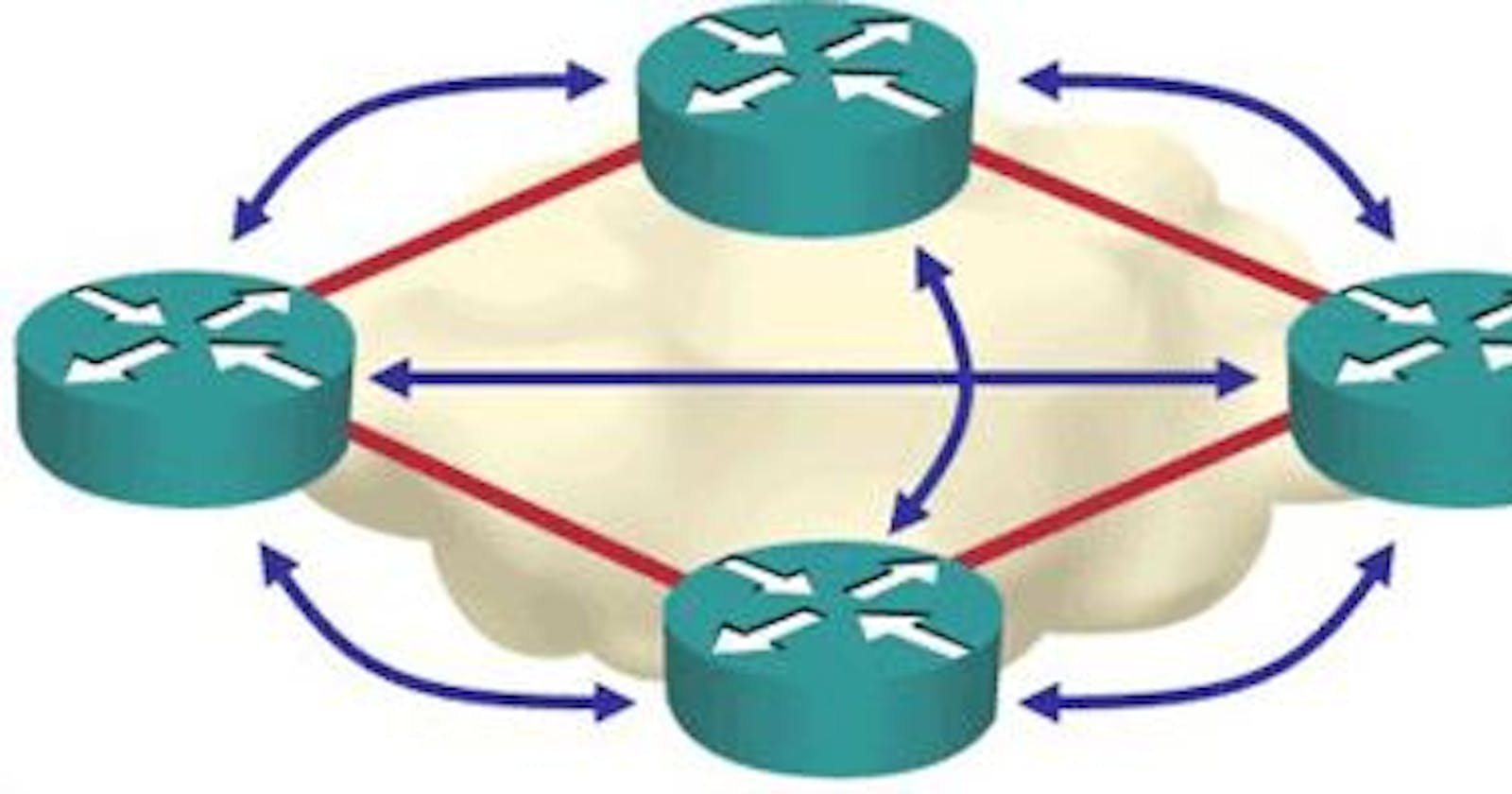
 Fig 1: BGP Overview
Fig 1: BGP Overview
The Border Gateway Protocol or router is a Layer 3 routing protocol that uses the following protocols to function:
Transmission Control Protocol or TCP (i.e reliable communication layer)
User Datagram Protocol or UDP (i.e unreliable communication layer)
Internet protocol or IP (i.e network layer communication)
It was designed to maximize routing efficiency, reduce the size of routing tables and to work with other routing protocols, such as OSPF, IS-IS, and EIGRP. It allows for communication between networks that are not directly connected and offers several mechanisms for accomplishing this. It can be used to interconnect different types of networks such as virtual private networks (VPNs) including IPv4, IPv6, and on open or proprietary networks.
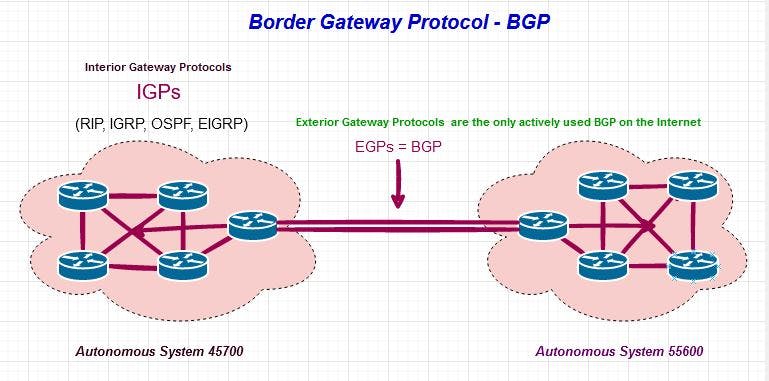
The Border Gateway Protocol is divided into two different types called the exterior routing protocol (EGP) and the interior gateway protocol (IGP). The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) can be used in different scenarios such as providing internet access to a remote location, allows devices to connect to the internet or to route data from one business entity or organization to another.
Types of Border Gateway Protocols
There are three types of Border Gateway Protocols:
Interior gateway protocol (IGP): This is designed to redistribute routing and shortest path information within an autonomous system.
Exterior gateway protocol (EGP): This is designed to exchange routing and shortest path information between autonomous systems (AS) on the internet.
Multi-homed border gateway protocol (MBGP): This is used in the Internet Protocol (IP) to exchange routing and shortest path information between autonomous systems (AS) on the internet. This protocol is designed to support various features, including proxy routing, advanced multipath routing, and policy routing.
Fig 2: Types of Border Gateway Protocols
Features of the Border Gateway Protocol include:
Autonomous System (AS) Routing tables - What are they? : Autonomous system (AS) is a network of systems, connected to one another and to the Internet, that runs its own routing protocol. An autonomous system is identified by a unique AS number and a unique autonomous system number.
These Autonomous System (AS) Routing tables are a collection of routing and static routing protocols that a given AS uses to route and determine the best path to a destination. They are primarily used by routers and network devices.
- BGP Decision Process : The BGP Decision Process is a process in the operation of BGP that is responsible for selecting the best path. The process is designed to select the route with the best combination of network conditions, such as the least number of hops, least cost, and shortest path. The process is also designed to make sure that the best path is consistently selected.
- BGP Peer : This is a device that participates in the BGP routing process. Two BGP speakers that form a TCP connection between one another for the purpose of exchanging routing information are referred to as neighbours or peers.
This is typically a router, but can be any type of device. Peers exchange information about the networks they are connected with in order to determine the best path for sending traffic. When connected to a BGP peer, a router can advertise networks it is connected with and the networks that are closest to the router.
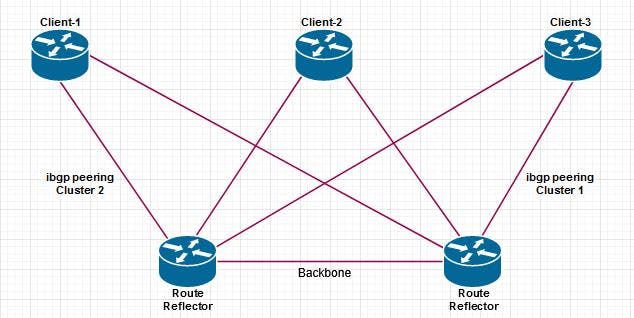
Fig 3: BGP Peering Session
BGP route reflector - What it is :
A BGP route reflector is a BGP instance or device that receives routing information from one or more routing protocols, and redistributes them to other routing protocols. A route reflector can also filter routing information based on different criteria and modify the routing information.What does a BGP route reflector look like? : A BGP route reflector usually has a lot of routers connected to it. The route reflector has a few interfaces, each with a different protocol, such as an Ethernet interface, a routing protocol, and an IPv6 interface. The route reflector will have a few route servers, which are used to manage routes. The route servers will store information about all of the routing protocols, and will distribute the information to other route servers.
Fig 4: BGP Route Reflectors
How Does BGP Work?
Since the Internet is made up thousands of networks called Autonomous Systems (ASes). A single organization or business entity controls each Autonomous System (AS). However, some institutions control more than one Autonomous System (AS) at a time. These Autonomous Systems exchange routing information with each other using a routing protocol called Border Gateway Protocol (BGP).
The Border Gateway Protocol relies on the transport protocol (i.e the TCP or UDP layer) port 179 to provide a connection to send traffic to the correct destination. Within an Autonomous System (AS), an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) handles routing and the routing information is shared between border routers using internal Border Gateway Protocol (iBGP). These routing information is exchanged using update messages. Each update message can contain route advertisements, route withdrawals or keep-alive messages.
BGP information is published in the BGP routing table. Routers that run a BGP routing process are often referred to as BGP speakers. The Border Gateway routers combine information from both IGP and BGP to create a forwarding table. The BGP routing table is a list of prefixes that are received by a router and their corresponding next-hop addresses.
In order to connect to a router using BGP, you must have a valid BGP session with the router. The Border Gateway Protocol marks the source of an internet packet or data and specifies the network layer address of the source. Then it sends individual messages back and forth via the internet, until they agree on a common routing path. This allows for better route selection and easier local routing decision making.
At this point, a BGP session is established by carrying out a three-way handshake between the peers. In other words, the Border Gateway Protocol is composed of three components:
The Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP)
The Autonomous system (AS) routing tables, and
The BGP decision process.
When sending traffic across the internet via a router, the Border Gateway Protocol which is a standard exterior gateway protocol will automatically deliver traffic to the next router. This can make it easier to send traffic through the internet as it will simplify the path your traffic takes across the internet.
The Autonomous system (AS) routing table is used to determine the best route to a given network or host. If a router receives a route that is not present in the routing table, it will reject the route. If this happens, the router sends a message to the local gateway. The local gateway then sends a message to the router to delete the invalid route.
Since, BGP is a path-vector routing protocol, it will determine the shortest path the data packet has to travel based on the distance to the destination of the receiver network. With the help of Route reflectors placed at strategic locations in the internet, the route reflectors continuously announce their routing table to the data packets. This is done by sending a copy of the table to a neighbouring route reflector. When the packet is sent to the next router, the route reflector will send a copy of the table to the neighbouring router.
High Performance Networking - The BGP Tuning Capabilities
In order to maintain high network performance, a BGP feature called BGP Tuning Capabilities can be used. With BGP Tuning Capabilities, BGP will attempt to make best routing decisions. This is important because it will prevent routing loops and IPv4 address exhaustion.
You can tune your BGP sessions to increase performance. For example, you can set the timers, max sessions, or min hold time to increase performance. You can also adjust the max prefixes or min prefixes in the Border Gateway Protocol settings to increase performance. The Border Gateway Protocol settings are found in the TCP/IP properties window in the Advanced properties section.
Benefits of Border Gateway Protocol
The several advantages of the border gateway protocol are:
It defines how autonomous systems are identified and how they are assigned a unique Autonomous System Number (ASN)
It is used by large companies to provide internal routing within their organizations
It is a fundamental part of the Internet's infrastructure
It is designed to allow a single routing protocol to be implemented in different countries and regions, while retaining the capability to route globally
It operates in a hierarchical, peer-to-peer network of individual routers
It makes possible to use routing protocols that are not native to the network or that are not supported natively by the network
It maintains the stability of internet routing and avoids network loops
The Border Gateway Protocol security feature (BGPsec)
BGPsec is a security technology feature that secures the BGP router with a cryptographic key. It is a layer 3 protocol that is deployed with BGP to provide authentication and integrity between autonomous systems. It is also used to prevent certain types of attacks such as spoofing and to ensure that the origin of the data is from where it claims to be from.
BGPsec provides encryption, data authenticity, data origin authentication and message integrity. This is important because it is used by the Internet and Cloud Service Providers to route traffic.
Cost of Border Gateway Protocol compared to other routing protocols
When you are looking at routing protocols, one of the most important factors to consider is cost. The Border Gateway Protocol is one of the most popular and cost effective protocols on the internet. What is most impressive about the Border Gateway Protocol is that it is considered a "best-effort" protocol. This means that it is able to provide a routing service even if the network that it is operating on is down.
In contrast, other routing protocols are unable to provide service if the network is down. This is because those types of protocols attempt to provide "zero-error" routing. The Border Gateway Protocol, on the other hand, is capable of providing a routing service even if the network becomes congested or contains errors.
The Impact of BGP on Businesses
The impact of BGP on businesses is immense. The main benefit for businesses is:
The ability to scale
Many businesses are able to save money and increase revenue by using BGP, which is a core component of their infrastructure
Access to all of the major internet and cloud service providers to increase business reach using the internet
To maximize revenue by providing customers with a wide variety of content
To better protect customer’s privacy by controlling the information those customers receive
A single connection for all of their customers and this allows for better customer services and faster customer response times
To keep track of what other businesses are doing and what routing information they are using
The future of Border Gateway Protocol
The future of the Border Gateway Protocol as a tool used to make the internet more stable and easier to manage will be shaped by the following:
Exponential growth in internet use estimated to be more than 8.5billion users after 2022
Segmentation of the internet to smaller networks for manageability and stability
Evolution of segmented internet networks as virtualized networks that can be attached to a real network
Conclusion
I hope you enjoyed this blog post about Border Gateway Protocol. While the BGP is a protocol that is the foundation of the internet, it allows businesses and internet/cloud service providers to route traffic across vast networks and to stay connected with their customers around the world.
This makes the Border Gateway Protocol a powerful tool for those looking to improve their connectivity and network performance as efficiently and cost effectively as possible.